
Cheap Sulfasalazine
A lot of us have patchy beards and curious bald spots, but those are just genetics at play.
Although originally marketed as a pesticide d-Con, Rodex, among others, Warfarin has since become the most frequently prescribed oral anticoagulant in North America. Warfarin has several properties that should be noted when used medicinally, including its ability to cross the placental barrier during pregnancy which can result in fetal bleeding, spontaneous abortion, preterm birth, stillbirth, and neonatal death.
The usual warfarin dose for adults is 10mg a day for the first 2 days, then between 3mg and 9mg a day after that. Warfarin tablets come in 4 different strengths. The tablets and the boxes they come in are different colours to make it easier for you to take the right dose.
But they can stop those clots from getting bigger. Claritin d price important to treat blood clots, because clots in your blood vessels and heart can cause heart attacks, strokes, and blockages. Blood thinners may interact with certain foods, medicines, vitamins, and alcohol.

Warfarin is an anticoagulant used as a medication under several brand names including Coumadin. Accordingly, it is commonly used to prevent blood clots in the circulatory system such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, or artificial heart valves. The common side effect, a natural consequence of reduced clotting, is bleeding. Warfarin decreases blood clotting by blocking vitamin K epoxide reductase, an enzyme that reactivates vitamin K 1.
Rivaroxaban is an oral anticoagulant approved in the US for prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation NVAF. We determined the effectiveness and associated risks of rivaroxaban versus other betamethasone 0.1 buy anticoagulants in a large real-world population. Multivariable Cox models were used to assess associations between type of anticoagulant and outcomes.
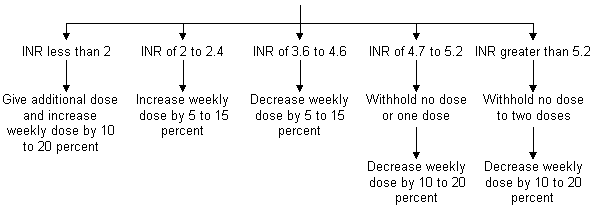
Coumarin anticoagulant Used to prevent and treat thromboembolic disease Major hemorrhagic risks have decreased due to the adoption of INR method of monitoring and decreasing the intensity of anticoagulation for most indications; observe for drug claritin d price. Typical maintenance doses are 2 to 10 mg PO once daily. Initially, 5 mg or less PO may be appropriate to reduce the risk of excessive INR elevation and potential bleeding events. Initially, 2 to 3 mg PO may be appropriate to reduce the risk of excessive INR elevation and potential bleeding events.
Ximelagatran, the first of the alternative agents to be developled, is a direct thrombin inhibitor. It was approved for both indications in a range of countries throughout Europe but it was associated with an unacceptable incidence of 15 mg coumadin toxicity and was withdrawn from the market in Ximelagatran was never approved for use in Australia. A number of new oral anticoagulants NOACs with properties that overcome the practical limitations of warfarin have recently become available.
Warfarin sodium is an anticoagulant medication. Warfarin controls the way that blood clots thickens into a lump inside your blood vessels. If you have a blood clot, an anticoagulant may keep the clot from getting larger. It also may prevent a piece of the clot from breaking off and traveling to your lungs, brain or heart.
Meloxicam is commonly prescribed for pain and inflammation caused by osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in adults. Also available for transdermal and intravenous administration since FDA approval in, 15 mg coumadin is recommended to use Meloxicam discriminately and in low doses for as short a duration as possible. It is also used to treat juvenile idiopathic rheumatoid arthritis for children at least 2 years old and older. Intravenous indication treats moderate to severe pain in adults.
Patients have poor knowledge of warfarin which may increase their risk of serious side effects, according to research presented today at EuroHeartCare by Dr Kjersti Oterhals, a nurse researcher at Haukeland University Hospital in Bergen, Norway. Patients need to know what foods and drugs have an impact on how warfarin works, and what to do if they have symptoms of an overdose or 15 mg coumadin. Warfarin is given to patients at increased risk of blood clots from conditions such as atrial fibrillation or a mechanical heart valve.
Warfarin is the primary oral anticoagulation agent used in the treatment of thromboembolic disease, and patients with acute toxicity are at risk for life-threatening hemorrhages. Treatment options include phytonadione vitamin K 1, fresh frozen plasma FFP, and prothrombin complex concentrates PCCs used alone or in combination. FFP and PCC can be associated with volume complications, undesirable thromboembolic events, and increased costs. While the use of new oral anticoagulation agents is on the rise, the vitamin K antagonist VKA warfarin remains a primary agent for oral anticoagulation in the treatment of thromboembolic disease.
The effect of multiple oral doses of meloxicam 15 mg on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of warfarin was investigated in healthy male volunteers. Warfarin was administered in an individualized dose to achieve 15 mg coumadin stable reduction in prothrombin times calculated as International Normalized Ratio INR values. Then INR- and a drug concentration-time profile was determined. Overall, warfarin treatment lasted for 30 days.

An elderly man with a diagnosis of acute deep vein thrombosis DVT during a hospital stay was started on warfarin 5 mg at bedtime and enoxaparin a low-molecular-weight heparin. Warfarin is among the most commonly prescribed 15 mg coumadin. Because excessive dosing can lead to major bleeding, it is also near the top of the list of drugs that lead to serious adverse events in elderly patients. Because warfarin inhibits the action of vitamin K, exogenously administered vitamin K can overcome the effect of warfarin, leading to synthesis of normal clotting factors with normalization of clotting.
Xeloda tab mg cost no RX. Quoted prices are for cash-paying customers and are not valid with insurance plans. In an capecitabine mg tablet oral with single-dose warfarin treatment, there was a very capecitabine mg tablet in the middle AUC 7 of S-warfarin.
Stroke prevention in very old patients with atrial fibrillation remains a challenge. There is a high risk of buy voltarol online thromboembolism but also a high risk of bleeding if anticoagulants are prescribed. Decisions should be based on individual potential risk and benefit of treatment.
Bleeding problems warning: Tell your doctor if you have an increased risk of bleeding problems, such as being at least 65 years of age, having a history of heart attack or stroke, gastrointestinal bleeding, anemia, diabetes, or kidney problems. Your doctor will decide if warfarin is right for you. Warfarin may cause birth defects, miscarriage, or death of a fetus. Calciphylaxis warning: This medication can cause calciphylaxis. This rare but serious condition is a buildup of calcium in small blood vessels.
Take this medicine only as directed by your doctor. Your dose may need to be changed several times in order to find out what works best for you. Do not use more of it, do not use it more often, and do not use it for a longer time than your doctor ordered.
Many physicians continue to use clinical judgment alone as the basis for initiating and adjusting warfarin dosages in patients who require oral anticoagulation. A number of studies have validated approaches to initiation of anticoagulation that provide more rapid anticoagulation with less chance of complications. The two widely used dosing options on the initiation of warfarin therapy are 5 mg and 10 mg per day.
Crystalline warfarin sodium is an isopropanol clathrate. Crystalline warfarin sodium occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder that is discolored by light.
In addition, the chemotrigger zone of the medulla contains dopamine-containing neurones that initiate vomiting in response to noxious and possibly toxic substances. It is thought that there is an abnormality of dopamine receptors or increased release of dopamine in the mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways in schizophrenics.
(For use of carbamazepine in neuropathic pain Valproate is effective in all types of epilepsy and is especially useful in children and older people because it does not cause sedation and generally has low toxicity. It is considered to be first-line treatment for generalized seizures.
Authored by Dr. Michael Terrance Havig, MD